At the Synaptic Level…
Alcohol affects the brain by altering the neurotransmission of Glutamate, GABA, and endogenous opioids.
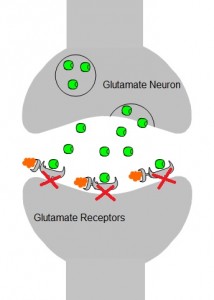
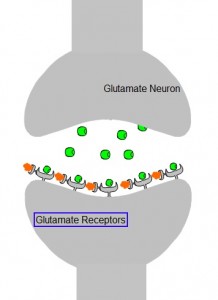
Glutamate:
-Glutamate (Glu) is the primary excitatory NT in the CNS.
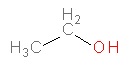
-Upon acute exposure, ethanol non-competitively inhibits glutamatergic neurotransmission through NMDA/AMPA receptors.
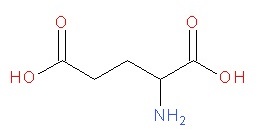
-After chronic use, neurons upregulate Glu receptors to attempt to maintain normal receptor activity even in the presence of ethanol.
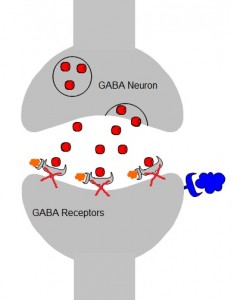
GABA:
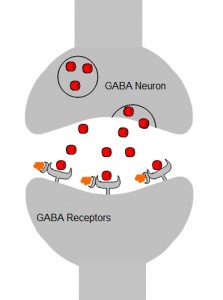
-GABA is the primary inhibitory NT in the CNS.
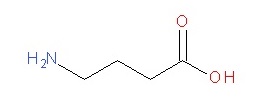
-Upon acute exposure, ethanol indirectly enhances GABAergic neurotransmission through an unknown mechanism of action, although indirect binding to the GABA receptor and phosphorylation cascades have been suggested.
Opioids:
-Ethanol increases the release of Beta-endorphin from the pituitary and hypothalamus
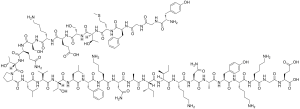
-This endogenous opioid acts on the opioid mu-receptors of GABAergic neurons and directly inhibits GABAergic neurotransmission.