Economic Analysis:
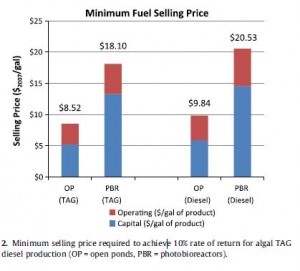
The main difficulty regarding algae fuels is the optimization of the process to reduce cost. Algae fuel costs are certainly expansive as is typical of most fuel generation, but the difference between petroleum- based fuels and algae fuels is that petroleum fuels have infrastructure for refining while algae fuels require a substantial capital investment. The cultivation and extraction process can also be energy intensive. Figure 1 illustrates the selling price that algae fuel would need to be with only a 10% rate of return on the investment. TAG refers to the intermediate oil cost (before it is upgraded to diesel products). The projected prices for algae based clearly are not low enough to compete with petroleum based fuels, especially because the majority of the world’s transportation sector is designed to run on petroleum based products (Davis).
The U.S is diligently working towards optimizing algae as a fuel source. An example of the United States commitment to algae as a biofuel feedstock as fuel is the U.S Derangement of Energy was granted $44 million to National Alliance for Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts towards research on algae. There have been many estimates on the future of algae as a source of fuel and Figure 2. shows that OP production based on the different estimated technological improvements and optimization. The figure shows that if lipid content witnesses an increase of 50%, harvesting cost is cut by 50% and extraction cost is cut by 50 %. Further, operating costs can become as little as $2.27/gal of lipid (Rapier)
- OP: Open pond production of Algae
- PBR: Photobioreactor production
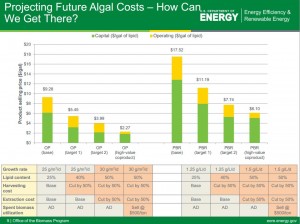
Rapier, R. (2012, May 7). Current and Projected Costs for Biofuels from Algae and Pyrolysis. Retrieved April 18, 2015, from http://www.energytrendsinsider.com/2012/05/07/current-and-projected-costs-for-biofuels-from-algae-and-pyrolysis/
There is high potential for third generation biofuels, specifically algae, but there is much more work to be considered. Many companies have invested millions of dollars to work on what some call the future of transportation fuels because of its extraordinary properties and benefits. Again, there is still an incredible amount to be done in order to create an optimized processand subsequently become relevant in a highly competitive transportation fuel industry.
(Composed by Eli Karp, edited by Robert King)
References:
http://www.takepart.com/article/2014/06/18/how-tiny-algae-could-be-future-carbon-free-fuels
http://www.biomassboard.gov/pdfs/tac_design_case_haq.pdf
Davis et al., R. (2011). Techno-economic analysis of autrophic microalgae for fuel production. Applied Energy, 88, 3524-3531. Retrieved April 19, 2015, from Elsevier
Rapier, R. (2012, May 7). Current and Projected Costs for Biofuels from Algae and Pyrolysis. Retrieved April 18, 2015, from http://www.energytrendsinsider.com/2012/05/07/current-and-projected-costs-for-biofuels-from-algae-and-pyrolysis/
