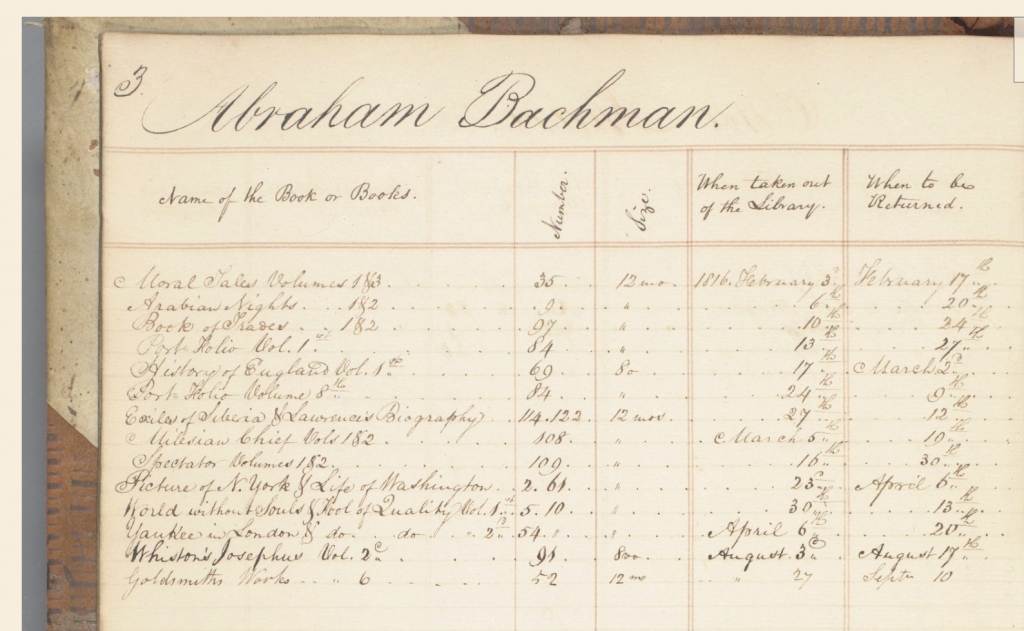
The Easton Library Company project began as an archival project with Associate Professor of English Chris Phillips’ discovery of a set of 18th century library ledgers at the Easton Area Public Library. The ledgers held the detailed records of the patrons of the Easton Library Company, the town’s original subscription library, and presented a bevy of data regarding the reading habits, community relationships, and family structures of Easton society. Yet this information was contained in fragile, aging ledger books accessible only to local residents.
Phillips, in collaboration with Digital Scholarship Services, began the enormous task of digitizing and transcribing these records with the help of a team of Excel Scholars: Gavin Jones ’14, Elena Principato ’15, Julia Campbell ’15, Cat Miller ’16, Eric Bockol ’16, Venita O’Hanlon ’16, and Sean Cavanagh ’16. Their hard work in deciphering 18th century librarian short hand and in researching local history forms the backbone of this project.
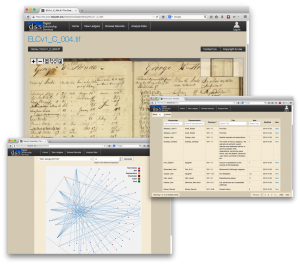
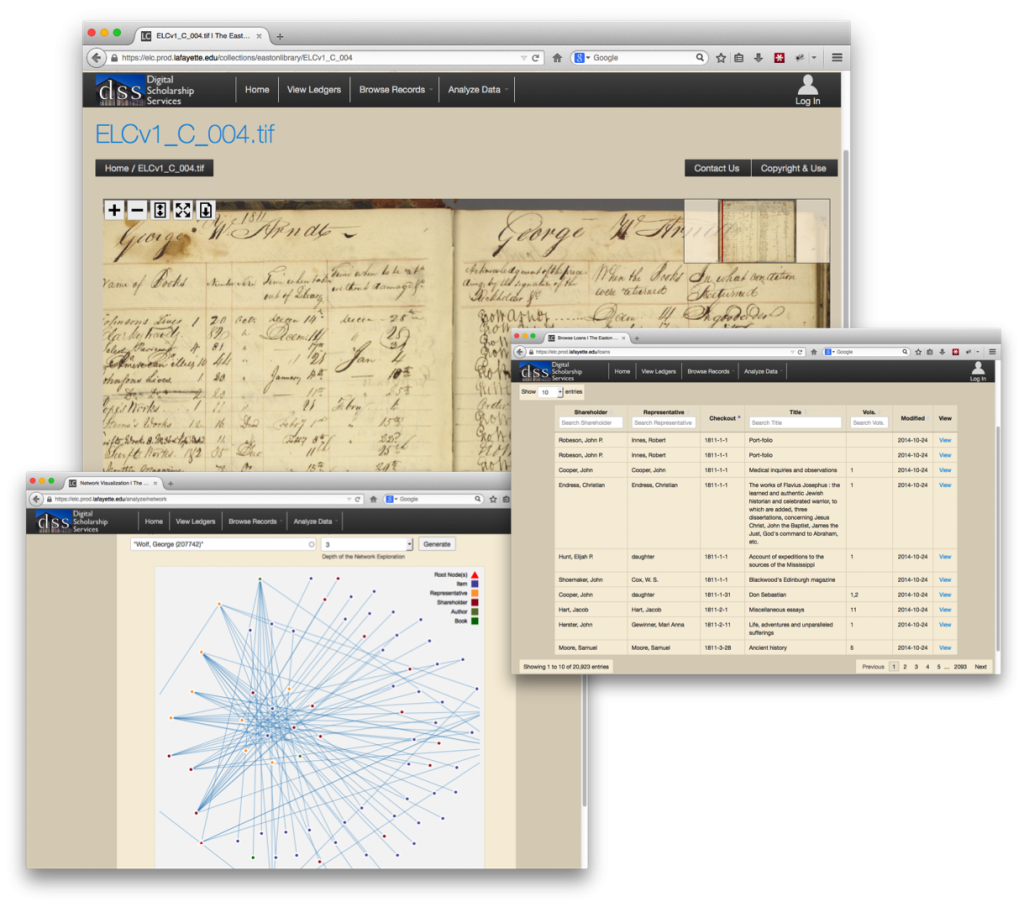
The long hours of work and analysis has now culminated in the launch of the Easton Library Company Database. Users can now browse through the ledgers digitized in high-resolution images and explore the reading habits of some of Easton’s most influential residents. The page images are linked to transcriptions that users can read alongside of the original page views.
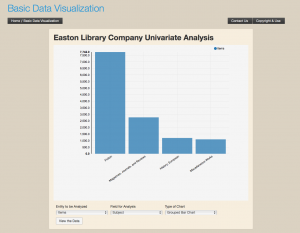
The information collected from these transcriptions forms the basis for the database. Visitors can also sort the contents of the database through a number of facets including book title, author name, and borrower name allowing a user to see who see who read a particular book, or all the books a particular person read. These same facets can be used to create visualizations of the data that reveal the patterns of reading and lending, and eventually the connections between community members. As more information is added to the database these visualizations will give users a glimpse into the social fabric of early Easton.
To create these tools and visualizations, DSS has made major improvements to the methods for entering new information into the database. Streamlining and refining the entry forms allows for easier data collection, and most importantly, they help to ensure the accuracy and standardization of new information, which then provides for better search results for the user.
The Easton Library Company Database is continually evolving and new data and new features will continue to be added to the site alongside of new research and information about the collection as it becomes available.
Explore the project at elc.lafayette.edu.
For more information on starting a digital project with DSS or applying for an internship opportunity contact us at digital@lafayette.edu , or call (610) 330-5796.