The means for using this solar energy comes via a solar collector. A solar collector captures solar radiation. Depending on the application different solar collectors are used.
Basic terms
Glazed – Solar collectors collect heat but absorbing heat through radiation. In order to reduce heat losses through convection and conduction, they are often covered in a transparent “glaze” that insulates the tubes.
Transmission fluid – A fluid that is heated in the tubes of the collectors and then circulates throughout the system to transmit heat. Typically air, water, or antifreeze is used.
Low Temperature Collector – A collector that operates at less than 110 degrees Fahrenheit. These are typically used for space heating and for heating pools
Medium Temperature Collector – A collector that operates between 140 and 180 degrees Fahrenheit. These can also be used for space heating but also for air conditioning.
High Temperature Collector – A collector that operates over 180 degrees Fahrenheit. This is used for electricity generation, and is also called Concentrated Solar Electricity generation.
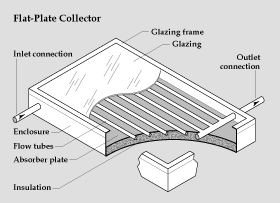
Flat Plate Collector
In 1950, Hottel and Whillier developed the flat plate solar collector. It is a commonly used technology in the application of solar water heating. The flat plate collector contains a dark, flat plate absorber to absorb incoming solar radiation. underneath the plate is an array of copper tubes containing a transmission fluid.The absorber itself is consists of a sheet mixed with thermally stable polymers, aluminum, steel or copper, and coated with a matte black or selective coating.
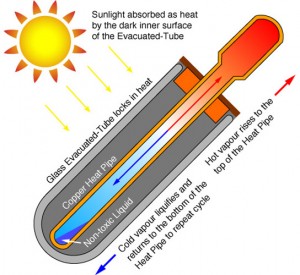
Evacuated Tube Collector
Evacuated tubes, or vacuum tubes work on the basic principle that heated fluid will rise. The collector has several glazed tubes that are exposed to the outside. They are not covered by anything like the flat plate collector. The tubes themselves are dark in color to attract radiation. The tubes are sealed on the bottom and open on the top. When heated, the transmission fluid rises to the top. It can then circulate throughout the system heat the target and then it will return to the tubes. When it returns it will be cold, and so it will sink to the bottom of the tube to be heated again.
Transpired Air Collector
A black plate covers a large reservoir of ambient air. The air is heated and directly pumped throughout a building. These are very simple and are not typically glazed. 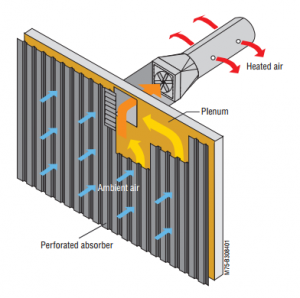
Authored by Sean Murphy
Edited by: Chris Castello
good post.Ne’er knew this, appreciate it for letting me know.
Hello There. I discovered your blog the use of msn. That is an extremely neatly written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and return to learn extra of your helpful information. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.