- All animal care and testing obeyed the rules of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at Lafayette College
- 13 red-eared slider turtles were purchased from Kons Scientific Co., Inc.
- Turtles were kept in 60 gallon tanks with island bricks for sunning
- Room temperature was kept at 28°C
- The room was kept on at 12:12 light to dark hour cycle
- Turtles were fed a floating fish food diet every other day and their tanks were cleaned weekly
- Turtles were kept in 60 gallon tanks with island bricks for sunning
Iris Dissection for Preparation of Florescence in situ Hybridization
- Turtles were weighed and measured before they were euthanized with pentobarbital and then
 decapitated
decapitated
- After they were weighed, the turtles were dark adapted
- Changes in light intensity cause the movement of photoreceptors and melanin granules of the retinal pigment epithelium. This movement, or retinomotor response, makes it harder to separate the retina from the other tissue of the eye during dissection
- Dark adapting the eyes of the turtles helps prevent the retinomotor response from occurring, and therefore yields an easier retinal dissection
- After they were weighed, the turtles were dark adapted
- The irises and retinas of the turtle eyes were then harvested
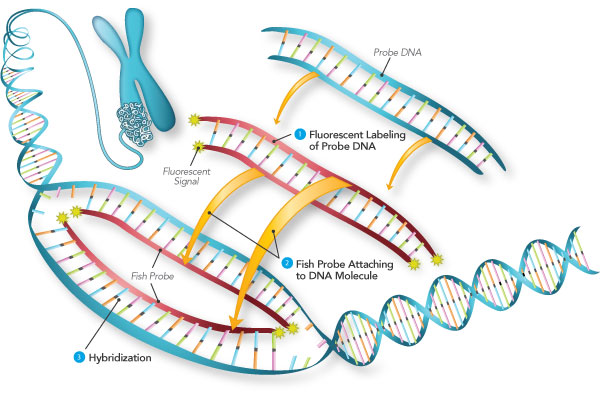
Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (fISH)
- Proteinase K was applied to the irises for 7 min. to make the tissues permeable.
- A pre-hybridization buffer was then applied to the tissue
- The microscope slides of fISH were enucleated in an opaque, humidifying chamber for 1 hour at 58°C
- Buffer was then added to the slides and the lid was placed on top to prevent the tissues from drying out
- Buffer was also added to the tissues every 10 min., for this same reason
- After a 1hr incubation period, excess buffer was removed from the slides, and the tissues were treated with sense or antisense probes
- Some of the tissues were hybridized without probes, to serve as a blank control group
- Sense probes served as controls for nonspecific binding, and blank controls were used to test for auto-fluorescence in the tissues
- Some of the tissues were hybridized without probes, to serve as a blank control group
- There were 2 types of antisense probes
- The first antisense probe was tagged with 6-FAM (fluorescein amidite), in order to detect the mRNA corresponding to the non-mammalian melanopsin form, Opn4x
- The second antisense probe was tagged with ATTo 550-NHS Ester, ATTO-TEC GmbH (Siegen, Germany), and was used to detect the mammalian melanopsin form, Opn4m
- All of the probes were produced commercially by Integrated DNA Technologies Inc.
- The probe sequences were chosen by using the company’s design algorithm for a qPCR primer. The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) was then used to test the probe sequences for specificity to Opn4x and Opn4m
- All of the antisense probes accurately matched the GenBank melanopsin sequences for the turtle (Opn4m and Opn4x). The antisense probes were also able to differentiate between the two melanopsin isoforms
- The probe sequences were chosen by using the company’s design algorithm for a qPCR primer. The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) was then used to test the probe sequences for specificity to Opn4x and Opn4m
- Once the probes were applied to the fISH slides, coverslips were placed over the tissues and the sliders were incubated for 16 hours at 60°C
- Cover slips and excess buffer solution were then removed, and the tissues were washed thoroughly
Confocal Microscopy & Statistical Analysis
- The fluorescence images that were produced by the probes in the iris tissues were isolated by using the equipment affiliated with the confocal microscope
- The fluorescence images were analyzed using the program FIJI (Fiji is just image J), in two different ways:
- The fluorescence yielded by the sense probes was subtracted by the fluorescence yielded by the images of the antisense probes. This was done in order to create a fluorescent image that reflected the binding of the signal of the probes to the melanopsin mRNA

Olympus FV10i Confocal Microscope (http://www.news-medical.net/FLUOVIEW-FV10i-Confocal-Microscope-Systems-from-Olympus )
- In order to account for the fluorescence yielded from nonspecific binding of the probe signal, the fluorescence yielded from the blank controls was also subtracted from the sense probe images
- To provide a quantitative analysis, the background and the florescence of each image were selected separately, so that the area, integrated density, and mean gray value could be measured using FIJI
- During this step, the corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) was calculated by multiplying the area of the fluorescent region by the mean grey value of the background, and then subtracting that product from the integrated density of the fluorescent region
- The fluorescence yielded by the sense probes was subtracted by the fluorescence yielded by the images of the antisense probes. This was done in order to create a fluorescent image that reflected the binding of the signal of the probes to the melanopsin mRNA
- A bar graph (Figure 4) was created in order to compare the mean CTCF values of the sense probes, antisense probes, and the blank controls
- T-tests and a one-way ANOVA were also performed in order to assess whether the fluorescence intensities produced in the sense and antisense slides differed
Eye Dissection and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
- Goal: To prepare irises for study, so that the location of the stained mRNA could be determined by using fISH
- The nuclei of the turtle eyes were removed and the eyes were bisected, using an incision
- The ciliary muscles, lens, and suspensory ligaments were then removed, so the iris could be seen more clearly
- Halves of the eyes, or eye cups, were viewed with an electron scanning microscope
- Before the tissues were mounted to the microscope slides, the liquid inside of the eyecups was removed, so that ice would not form on the top of the tissues
- Tissue Tek was used as a glue to mount the tissues to aluminum sample stubs and also as antifreeze, so the tissues did not fracture, while the sample was frozen
- The sample was frozen at -20°C, and then inserted into the microscope, where images were acquired