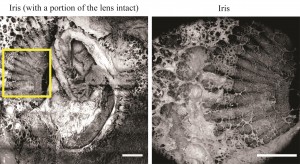
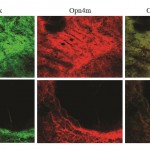
- The mRNA coding for Opn4x and Opn4m are both found in the iris of the turtle (Fig 1).
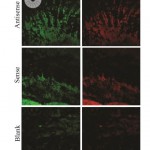
- This conclusion is supported by the calibration of signals (Fig 3) and the quantitative analysis that was performed, comparing the signals from the
antisense slides to those of the sense and blank slides
- The qPCR studies that were performed in Dr. Dearworth’s lab also support this finding (Dearworth et al., 2011; Goldberg, 2012; Dearworth et al., 2012)
- This result is consistent with prior studies performed on the Xenopus and the chicken, which are also non-mammals (Provencio et al., 1998; Chaurasia et al., 2005; Bellingham et al., 2006)
- This conclusion is supported by the calibration of signals (Fig 3) and the quantitative analysis that was performed, comparing the signals from the
- The dim fluorescence found in the blank and sense iris slides is likely caused by autofluorescence
- It is possible that the turtle iris has fluorescent pigments like the irises of birds (Tilloston & Oliphant, 1990)
- The likelihood of the presence of fluorescent pigments in the turtle iris is also increased by the fluorescent oil droplets that turtles and birds share (Ohtsuka, 1985)
- Both the Opn4x and Opn4m melanopsin isoforms appear to be found within the iris, sphincter, and dilator of turtle eyes, and they also appear to overlap
- This conclusion cannot be supported by the images produced by this study because it is not possible to distinguish the different types of muscle cells in those images
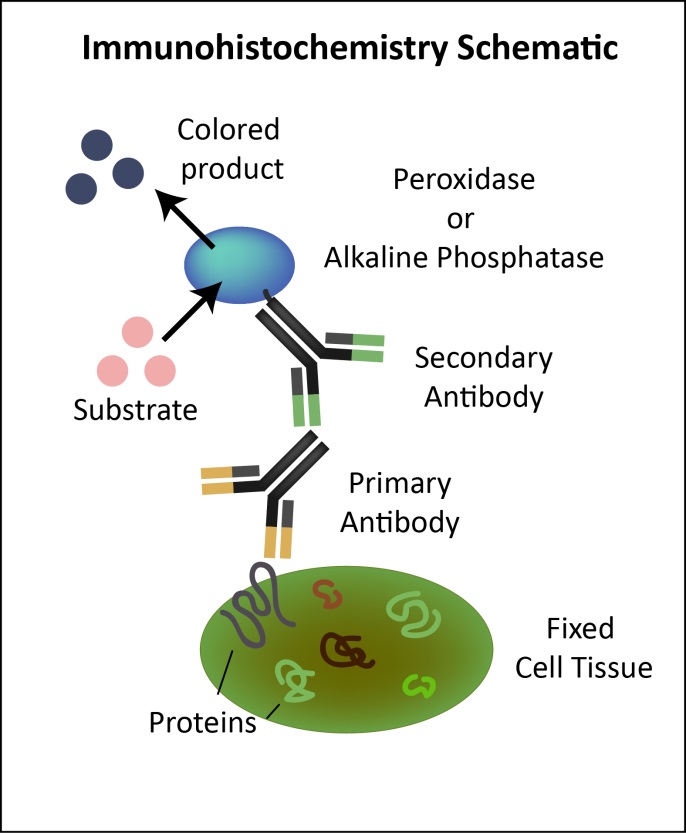
- It may be possible to identify the cell types that express the melanopsin isoforms by using a preassembled genome of the red-eared slider turtle, GenBank SRX217618, and then purchasing the antibodies necessary to carryout immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Using IHC experiments, the specific locations of the cells could then be identified, if probes are created that label for actin and Opn4x and Opn4m proteins
- By creating probes that label for actin, the type of muscle (smooth or skeletal) could potentially be distinguished, for they have difference muscle organizations
- Using IHC experiments, the specific locations of the cells could then be identified, if probes are created that label for actin and Opn4x and Opn4m proteins
- By identifying which cell types express the melanopsin isoforms, we could then possibly find an explanation for the slow pupillary light response that turtles demonstrate
- Although the presence of the melanopsin mRNA does not say for sure that the melanopsin isoforms are expressed, the evidence still supports this possibility