Click here to see a demonstration of the optic nerve fiber and caudal photoreceptor dissection
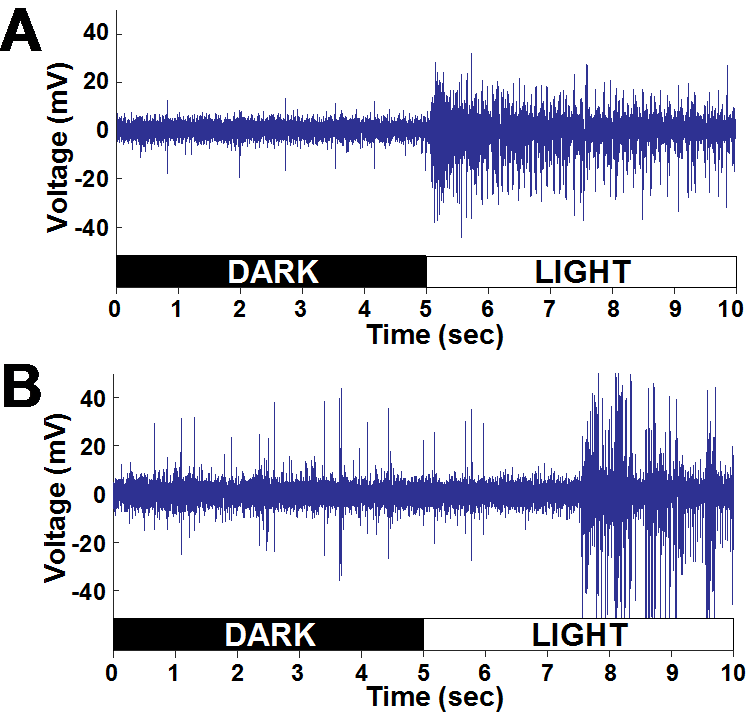
- Latencies of responses from the optic nerve fibers were much shorter than those of the caudal photoreceptors (75ms versus 2-3s)
- Mean firing rates were determined from five repeated trials
- The firing rates were measured for 5s in both the light and dark conditions
- This was performed for one preparation of the optic nerve fibers and the caudal photoreceptor
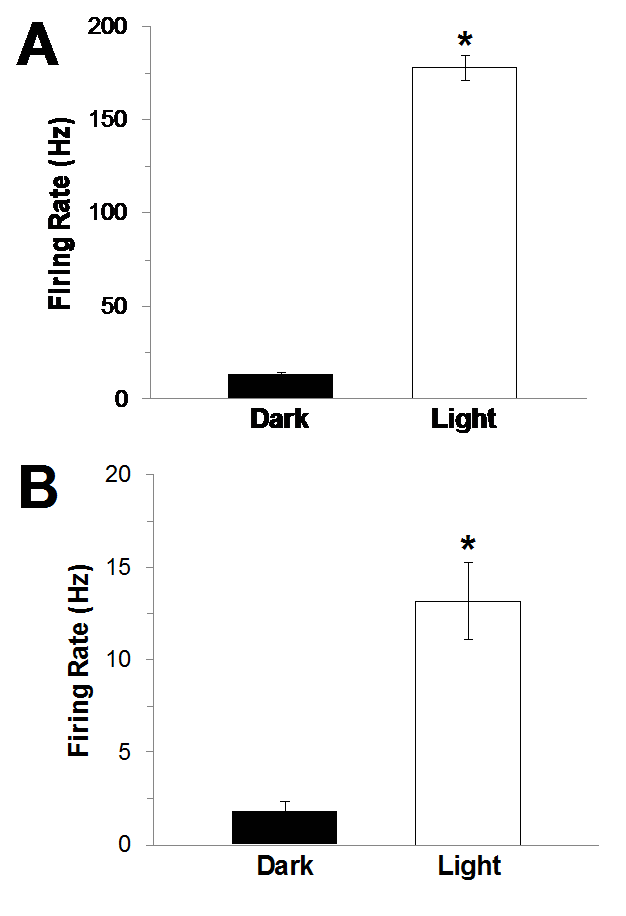
Figure 12A: Optic Nerve Fibers; Figure 12B: Caudal Photorecepto (Journal of Undergraduate Neuroscience Education)
- Firing rates were found to be greater for the optic nerve fibers than for the caudal photoreceptor
- Mean firing rate for optic nerve fiber
- Dark conditions: 13 +/- 1.3Hz
- Light conditions: 178 +/- 6.7Hz
- Mean firing rate for caudal photoreceptor
- Dark conditions: 2 +/- 0.6Hz
- Light conditions: 13 +/- 2.1Hz
- As expected, there was a significant difference observed between the firing rates during dark and light conditions of the optic nerve fibers and the caudal photoreceptor
- Optic nerve fibers (t=22; P<0.01)
- Caudal photoreceptor (t=6.7; P< 0.01)