What is a PHEV?
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) utilize an efficient combination of electric and gasoline powered motors to move the vehicle with reduced emissions. The battery packs in these vehicles are larger than those in traditional hybrids, and are charged by both regenerative braking and by being plugged into a wall socket. Figure 1, below shows a diagram of a generic plug-in hybrid vehicle.
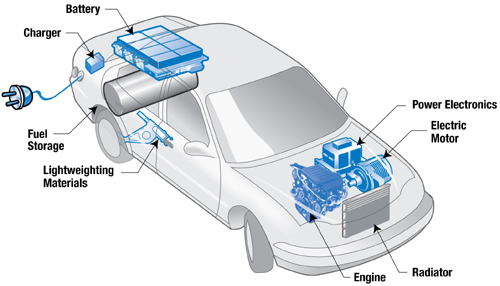
This diagram illustrates the flow of energy through the car, it originates as chemical energy stored in either the gas tank or battery. A variety of things could then happen based off of the type of drive-train in the vehicle. The three options from here are series, parallel or series-parallel drive-trains. Series systems only receive mechanical power from the electric motor, while in the parallel system the two engines work in tandem to provide mechanical power. Finally the series-parallel system allows for the two systems to work together or independently. These three scenarios are demonstrated in a clear energy flow graphic on this link. The following video provides a macroscopic summary of the benefits and drawbacks that are faced with PHEV’s.
Fact-sheet: PHEV1
References
Union of Concerned Scientists. How do plug-in hybrid electric cars work? Retrieved 4/19, 2015, from http://www.ucsusa.org/clean-vehicles/electric-vehicles/how-do-plug-in-hybrid-electric-cars-work#.VTQRp9VT628
US Department of Energy. Plug-in hybrids. Retrieved 4/19, 2015, from https://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/phevtech.shtml
Author: Justin Pié
Editor: Raji Gunasekera