Solar photovoltaic (PV) cells convert sunlight into DC (direct current) power. Particles of light, known as photons, emit from the sun and pass through the anti-reflective coating located on top of the cell. Beneath the anti-reflective coating are layers of conductors (including one negative and one positive) and a semiconductor layer. Crystalline silicon is the most commonly used material for the semiconductor in PV cells. When the photons of light strike the semiconductor atoms, negatively-charged electrons are “knocked” loose from the atoms, resulting in free electrons and positively charged ions of the semiconductor. The loose electrons are attracted to the negative conductor, while the ions are attracted to the positive layer. The flow of electrons generates an electrical DC current, which can then be redirected to power lighting, appliances, or almost anything else that uses electricity.
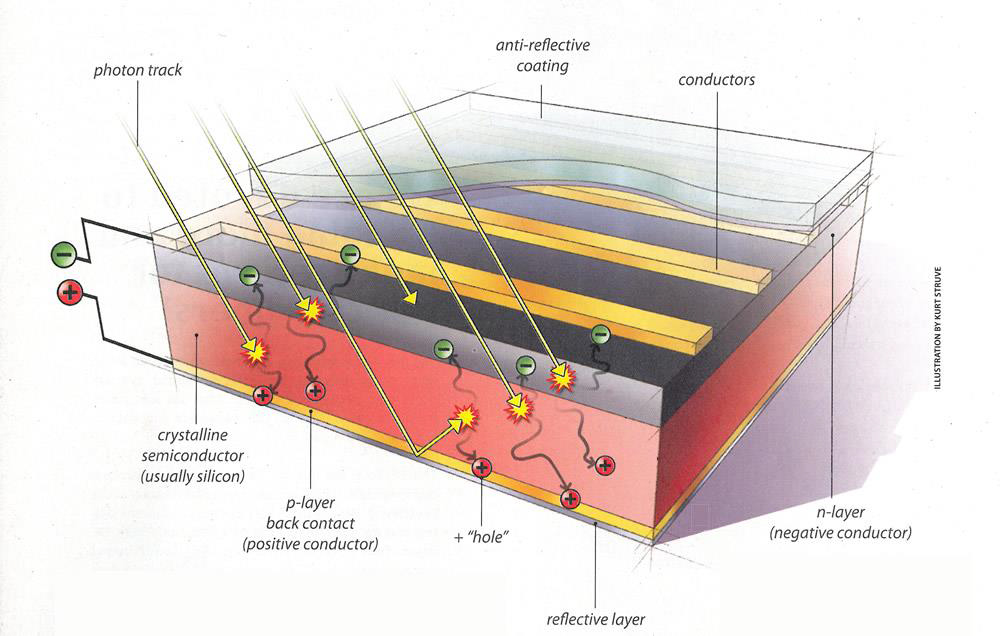
Image via Photovoltaic (Solar Electric). (n.d.). Retrieved from seia
Solar PV cells are arranged into arrays that make up familiar solar panels. Since the cells produce an electrical current, it is inefficient to store it for later use. Thus, solar PV systems are usually connected to the local electrical grid. For residential and commercial PV systems, the energy flows to an inverter, which changes the power from DC to AC (alternating current). This AC energy is what is used in household and commercial applications. The energy that is not used is sent to the electrical grid, so that it may be used for other purposes.
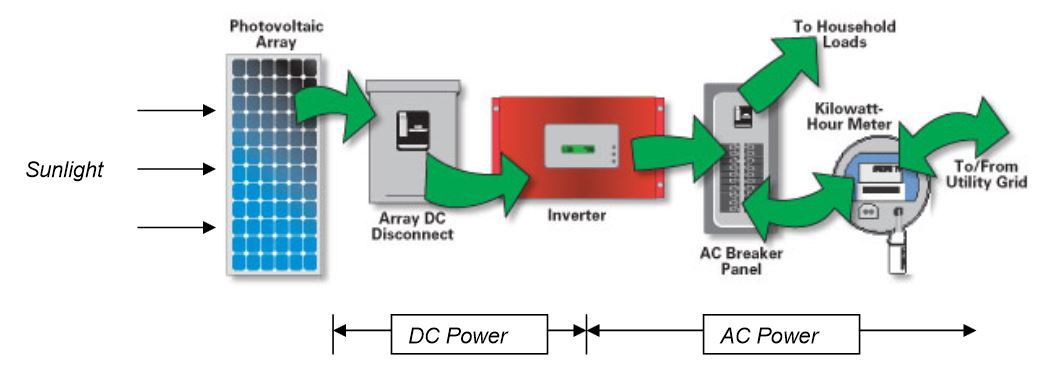
Office of Integrated Analysis and Forecasting U.S. Energy Information Administration. (2010). Photovoltaic (PV) Cost and Performance Characteristics for Residential and Commercial Applications: Final Report. Retrieved from eia
Author: Rick Cerretani
Editor: Abby Studen, Hannah Goldstein, Kevin Jackson
Sources:
Office of Integrated Analysis and Forecasting U.S. Energy Information Administration. (2010). Photovoltaic (PV) Cost and Performance Characteristics for Residential and Commercial Applications: Final Report. Retrieved from http://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/distribgen/system/pdf/appendix-a.pdf
Photovoltaic (Solar Electric). (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.seia.org/policy/solar-technology/photovoltaic-solar-electric