Clean Air Act of 1970
– First major air-quality act that directed the EPA to take steps towards improving air quality from “mobile” emitters
– Directed both state and federal emissions standards
Energy Policy Act of 1992
– Establishes “Alternative Fuels” as methanol, ethanol, and other alcohols; blends of 85% or more of alcohol with gasoline (E85); natural gas and liquid fuels domestically produced from natural gas; propane; hydrogen; electricity; biodiesel (B100); coal-derived liquid fuels; fuels, other than alcohol, derived from biological materials; and P-Series fuels
– Requires federal, state, and alternative fuel provider fleets to purchase alternative fuel vehicles
Energy Policy Act of 2005
– Requires federal fleet vehicles to use alternative fuels in dual-fuel vehicles
– Directs government agencies, in particular the DOE, to establish research grants for hybrid technology, and to bolster sales of hybrid vehicles via the use of incentive programs
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
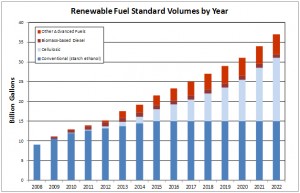
– Establishes renewable field standards (requires transportation fuel sold in the United States to contain a minimum of 36 billion gallons of renewable fuels annually by 2022)
Current and Future Policies and Standards
– CAFE Standards: Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards are standards that regulate the average fuel economies of typical consumer vehicles (cars and light trucks) sold in the United States.
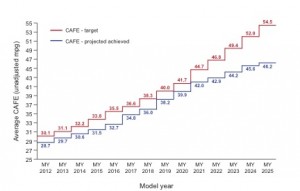
*SCHOETTLE, Brandon, and Michael SIVAK. A COMPARISON OF CAFE STANDARDS AND ACTUAL CAFE PERFORMANCE OF NEW LIGHT-DUTY VEHICLES. University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, n.d. Web. 4 May 2014. .
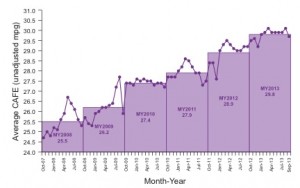
SCHOETTLE, Brandon, and Michael SIVAK. A COMPARISON OF CAFE STANDARDS AND ACTUAL CAFE PERFORMANCE OF NEW LIGHT-DUTY VEHICLES. University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, n.d. Web. 4 May 2014. .
– CO2 pollution from typical consumer vehicles since 1992
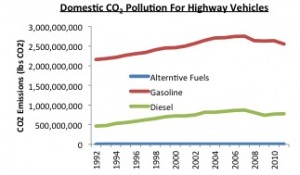
*Information from United States Department of Transportation, further citation included in Brandon Commodaro Fact Sheet
*Unless otherwise noted, all facts, figures, images and summaries were taken and formed directly from or in part by the individual reports in the title filed by the United States Department of Energy
Authored by: Brandon Commodaro