Types of CSP Devices
Parabolic Troughs:
Parabolic Troughs are made of solar collectors in the form of mirrors and heat receivers. These are parabolic shaped devices that concentrate incoming sunlight onto a central tube that lies on the focal line in the trough. Heat transfer fluid is then circulated through the central absorbing tube. This transfer fluid is usually a synthetic oil or molten salt.
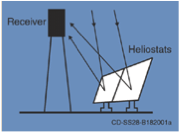
Solar Towers:
Solar Tower devices consist of a field of mirrors that direct incoming sunlight to a central receiver that then converts the received light into energy. The heat directed at the receiver powers a “thermodynamic cycle” which converts the energy into electrical power. This type of device uses water/steam or molten salt in order to power the turbines. Solar towers provide a higher efficiency with higher temperatures.
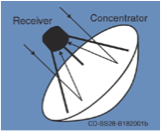
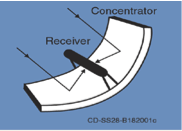
Dish Stirlings:
Dish Stirlings are parabolic dishes that are similar to satellite dishes in appearance. These stirlings reflect solar irradiation onto a receiver (either stirling engine or micro turbine) at the focal point of the dish. For this device to properly work, the Sun must be tracked in two axes. A dry cooling system is used within the system, which differentiates it from the other methods. In addition, dish stirlings are able to work properly on uneven terrain. This method possibly has the highest efficiency out of all of the CSP methods up to date.
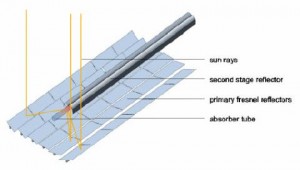
Linear Fresnel Collectors:
Linear Fresnel Collecters are very similar to Parabolic troughs. These collectors are made up of a series of long and flat/curved mirrors positioned at varying angles to concentrate sunlight to a receiver. The line of mirrors have a single-axis tracking system in order to ensure that sunlight is always concentrated on the receiver. Out of the other three methods of concentrated solar power, the linear fresnel collectors are a much cheaper process and are the easiest to assemble.
Written by: Dani de Lucio
Edited by: Michael Duncan
Information and Photos provided from:Concentrating Solar Power. (n.d.). Solar Energy Development Programmatic. Retrieved April 8, 2014, from http://solareis.anl.gov/documents/docs/NR
Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) Technology. (n.d.). Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) Technology. Retrieved April 8, 2014, from http://solareis.anl.gov/guide/solar/csp/
Concentrating Solar Power. (n.d.). IRENA. Retrieved April 9, 2014, from http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/RE_Technologies_Cost_Analysis-CSP.pdf