
Geothermal energy is harnessing the heat from the earth and using it for heating and converting into electricity. It is considered renewable because this heat source is constant and never ending.
Current Uses
There are three main types of geothermal energy technologies: Geothermal heat pumps, direct heating and electricity production, but the most common is electricity production.
- Geothermal Electricity Production: Generating electricity from the earth’s heat
Found below is a schematic of a geothermal power plant, where steam sourced from hot water deep inside the earth is powering a turbine which is attached to a generator, producing electricity.
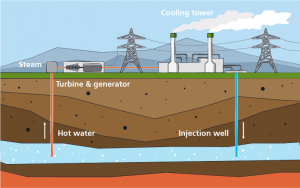
This is the typical process of many power plants in producing electricity, but most power plants are using fossil fuels in order to boil water for steam production. Geothermal power plants use steam heated from reservoirs of hot water found below the earth’s surface. The three types of geothermal power plants are: dry steam, flash steam and binary cycle.
Dry steam is when steam is piped from underground wells to the power plant. However, there are only two underground resources of steam in the US: The Geysers in California and Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming. Yellowstone is protected lands, so the only dry steam power plant is in California.
Flash steam uses geothermal reservoirs with water at a temperature greater than 360 degrees Fahrenheit. As it flows upwards, the pressure is decreased and some of the hot water boils to steam. The water and steam are separated and the steam powers turbines and the water is recycled back into the reservoirs. This is the most common type of geothermal power plant.
Binary cycle power plants use water at lower temperatures of approximately 225-360 degrees Fahrenheit and using a heat exchanger and a secondary liquid, the turbine is turned to power the generator.
Cost
Currently, at the Geysers in California, power is sold for $0.03 to $0.035 per kWh, and a power plant today would probably cost $0.05 per kWh. Power costs can also vary with high demand periods.
To drill a geothermal well it could cost $1 million to $4 million dollars and installing an at home geothermal pump could cost approximately $30,000 dollars but has the potential to cut energy bills by 30-40% and is estimated to have a payback period of 5-10 years.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Geothermal Energy:
- It is a reliable source of energy–unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal energy is always there and efficient
- There are no methane or carbon dioxide emissions from geothermal power plants
- The hot water reservoirs are renewable and sustainable as a source of energy
The majority of geothermal power plants are located in the West Coast of the United States because of the water reservoirs and their relative locations. Below is a map of the Hydrothermal sites and the favorability of locations.

Other disadvantages to geothermal energy include:
- High initial costs of building the power plant and instillation
- Environmental impacts of high water usage and release of sulphur dioxide released into the air and land
- Potential for causing earthquakes
Future Outlook
Geothermal is currently considered the fourth most significant type of renewable energy behind solar, wind, and hydropower. Geothermal energy is growing and has the potential to assist in becoming less dependent on fossil fuel resources. Some experts predict it may grow to account for 1/6 of the total world power supply, and others with a more conservative estimate predict it will account for approximately 4%.