
Solar Energy is one of the leading renewable energy technologies in the world today. People have been using the suns energy as a source for thousands of years for drying and storing food. In more modern times, researchers have developed the technology to trap the suns energy and convert it into electricity, turning the world’s rays into power.
How It Works
There are two types of solar energy: Photovoltaic (commonly referred to as PV) and Thermal. PV converts sunlight to electricity using solar panels comprised of semiconductor cells. Solar thermal technology captures the suns heat which is either used directly or converted first to mechanical energy and then to electricity. This type of technology is also referred to as concentrated solar power or CSP.
For photovoltaic panels, light hits a photovoltaic cell and is converted into electricity using a semiconductor. The semiconductor can be a variety of materials but a common semiconductor is silicon. A PV panel has several cells that produce a direct current which is converted into an alternating current by an inverter. This energy can then be stored, or used as a source for electricity.
Current Uses
There are currently 1.3 million solar instillations across the United States. This equates to a cumulative capacity of 40 gigawatts, or the equivalent of enough capacity to power over 6.5 million US households.
The number of solar instillations has increased dramatically in the past 5 years. A graph from the Solar Energy Industries Association shows the growth since 2000. This is correlated to the creation of the Solar Investment Tax Credit or the ITC.
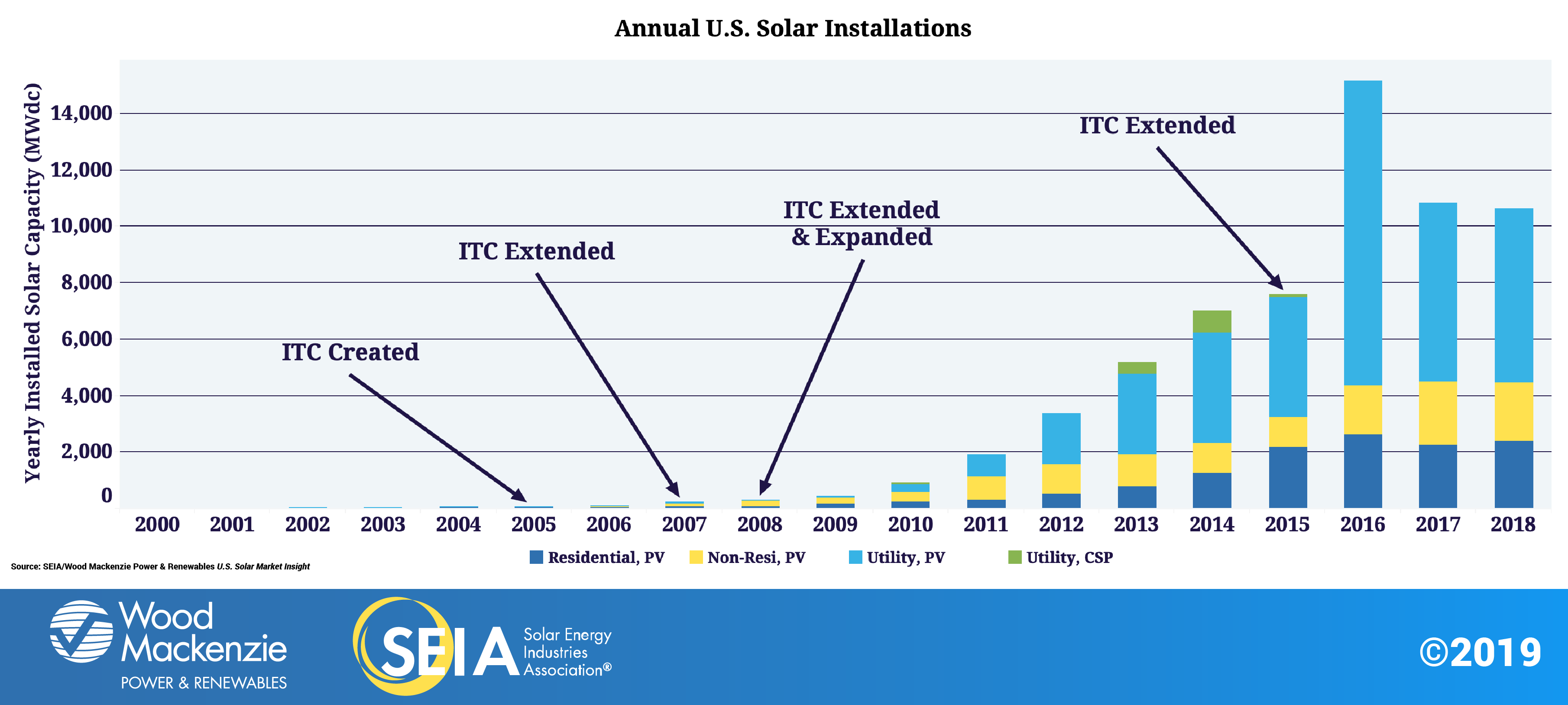
Cost
The rise in solar panel instillations is linked to a decrease in the cost of solar panels. This correlation can be seen below. 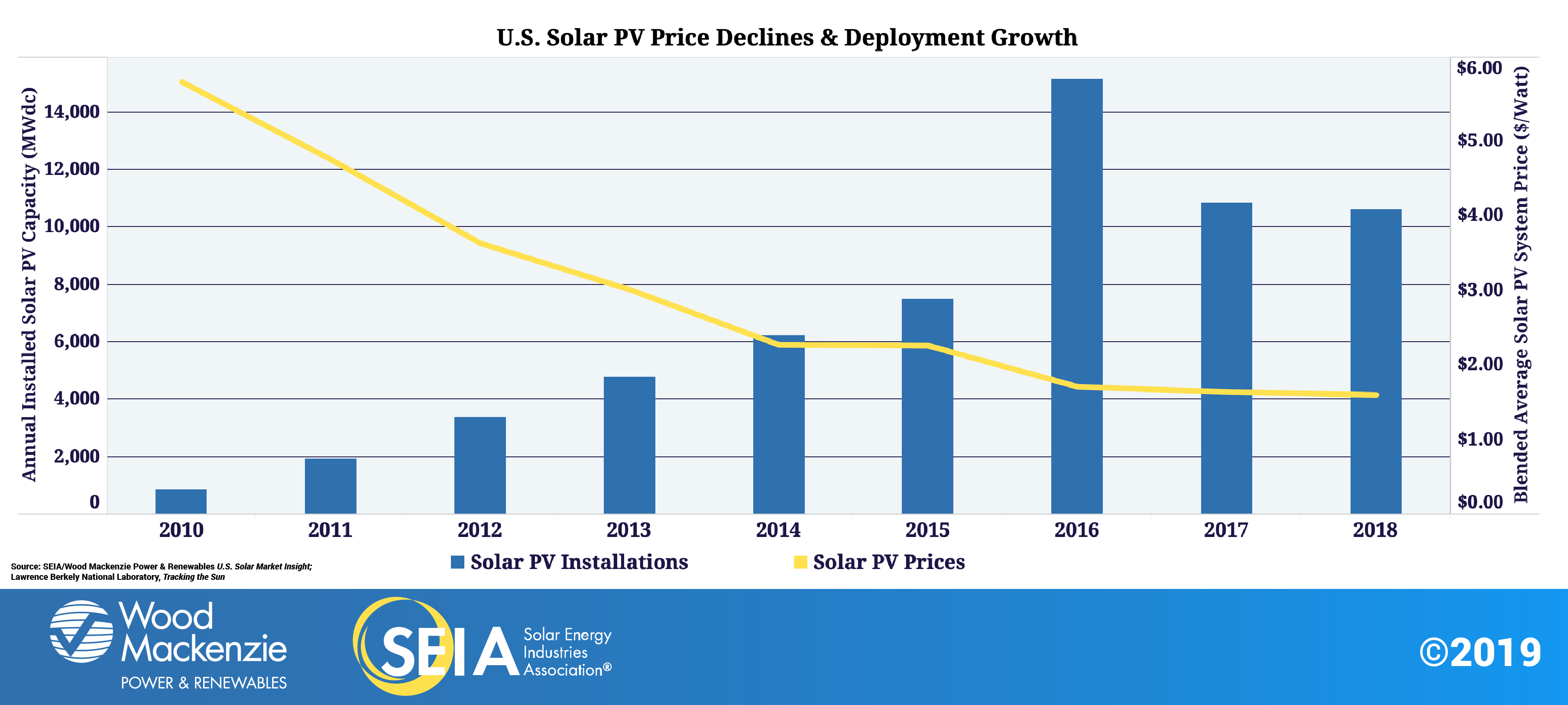
The price for a Solar PV System is now approximately $1.50 per Watt. This is economically advantageous and combined with the Investment Tax Credit, the payback period for residential PV panels has decreased dramatically.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main benefits of solar energy are:
- Solar energy does not produce air pollutants or carbon dioxide
- Solar energy systems on buildings have minimal effects on the environment
The biggest current limitations are:
- Sunlight as a source is not constant and not guaranteed. It can vary based on location, time of day, season, and weather.
- A large surface area is required to absorb a useful amount of energy
Future Outlook
Growth is trending upwards, and the amount of people employed in the solar energy industry has doubled since 2010. Prices for instillation are on the decline and technology is steadily advancing. The only deterrent to a bright future for solar energy is an administrative government who does not believe in or support combatting climate change. However, even with the pushback, solar energy has the potential and outlook to be scaled up to widespread use and is promising in becoming a nation less dependent on non-renewable sources.